Vitamin K Infographic with Concise Description
Vitamin K is a term which encompasses phylloquinone (vitamin K1), menaquinone (K2) and menadione (K3). Vitamin K1 is made by plants, vitamin K2 synthesized by bacteria in the intestines and vitamin K3 is made by humans in the laboratory.
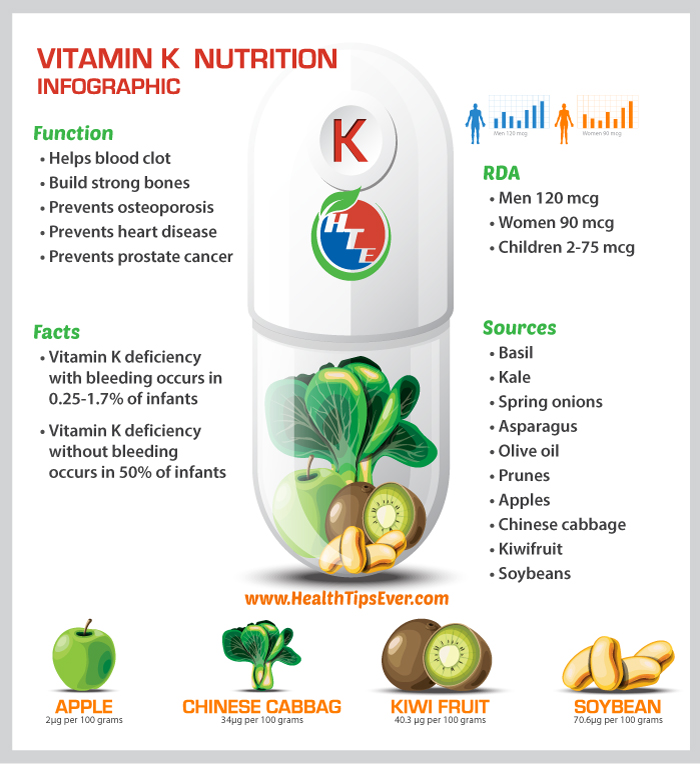
Vitamin K is a vital component for the blood clotting process in the body. The body also needs this vitamin when it is using calcium to build and maintain strong bones. It is also vital for preventing osteoporosis.
Vitamin K also helps prevent heart disease and cancer of the prostrate.
Contents
Sources of Vitamin K
Foods that are good sources of vitamin K include:
- Basil and other herbs and spices like chili powder, curry powder, paprika and cayenne pepper
- Kale and other leafy greens like spinach, mustard greens, collards, beet greens, Swiss chard, turnip greens and dandelion green
- Spring onions and other salad vegetables like garden cress, endive, radicchio, chicory greens, watercress, romaine lettuce, green lettuce, red lettuce, celery, arugula, iceberg lettuce and cucumber
- Asparagus, fennel, leeks and okra
- Olive oil and other vegetable oils like soybean and canola.
- Prunes and other dried fruits like blueberries, pears, peaches, figs and currants
- Apples
- Chinese cabbage(pak-choi) and other brassica vegetables like Brussel sprouts, broccoli, cabbage, red cabbage and cauliflower
- Kiwifruit
- Raw soybeans raw and roasted soybeans (Endamame) as well as fermented soy products like natto and miso
Other good sources of this vitamin include beef liver and wheat bran as well as fermented dairy products like cheese and yogurt. Green tea is another good source of this vitamin.
Foods that have been fortified with vitamin K are other great sources of this nutrient. Examples include some breakfast cereals and meal replacement protein shakes.
Recommended Dietary Allowance of Vitamin K
The recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for vitamin K is 120 mcg for men and 90 mcg for women.
This RDA can be provided by eating 1 ¼ cups of cooked soybeans or 1/10 cup of cooked kale.
The RDA for children is as follows:
- 0-6 months 2 mcg
- 7-12 months 2.5 mcg
- 1-3 years 30 mcg
- 4-8 years 55 mcg
- 9-13 years 60 mcg
- 14-18 years 75 mcg
Vitamin K Deficiency
Vitamin K deficiency is not common in adults since it is found in many foods and bacteria in the intestines also make it. However it is quite common in babies since they are born without bacteria in their intestines and they do not get adequate amounts of this nutrient from breast milk.
Symptoms of vitamin K deficiency include easy bruising, bleeding from the nose, gums and other parts of the body. Internal bleeding may manifest as blood in the urine and black stools.
Conclusion
Vitamin K is required by the body to help blood clot or coagulate properly and build strong bones. Foods which are good sources of this vital vitamin should therefore be consumed every day.